Infection process on Watts-Strogatz network of mixed agents
Abstract
The dynamics of a susceptible-infectious (SI) type of infection on a Watts-Strogatz (WS) network of inhomogeneous agents is simulated using an agent-based model. Starting from a regular lattice forming a probabilistic elementary cellular automata (pECA), a WS network realized by introducing the rewiring probability r which can be tuned to cover pECA (r = 0) and a fully random network (r = 1) cases. Each one neighboring infected agent provides an infection probability ρ to a susceptible agent. An expression for the effective probability of infection 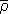 whenever there are n infected neighbors is derived. The time T90 it takes for the disease to spread until at least 90% of the population is infected was shown to follow a power law trend with respect to the infection probability ρ. An inverse relationship for completely random network is shown consistent with a derived analytic expression.
whenever there are n infected neighbors is derived. The time T90 it takes for the disease to spread until at least 90% of the population is infected was shown to follow a power law trend with respect to the infection probability ρ. An inverse relationship for completely random network is shown consistent with a derived analytic expression.















